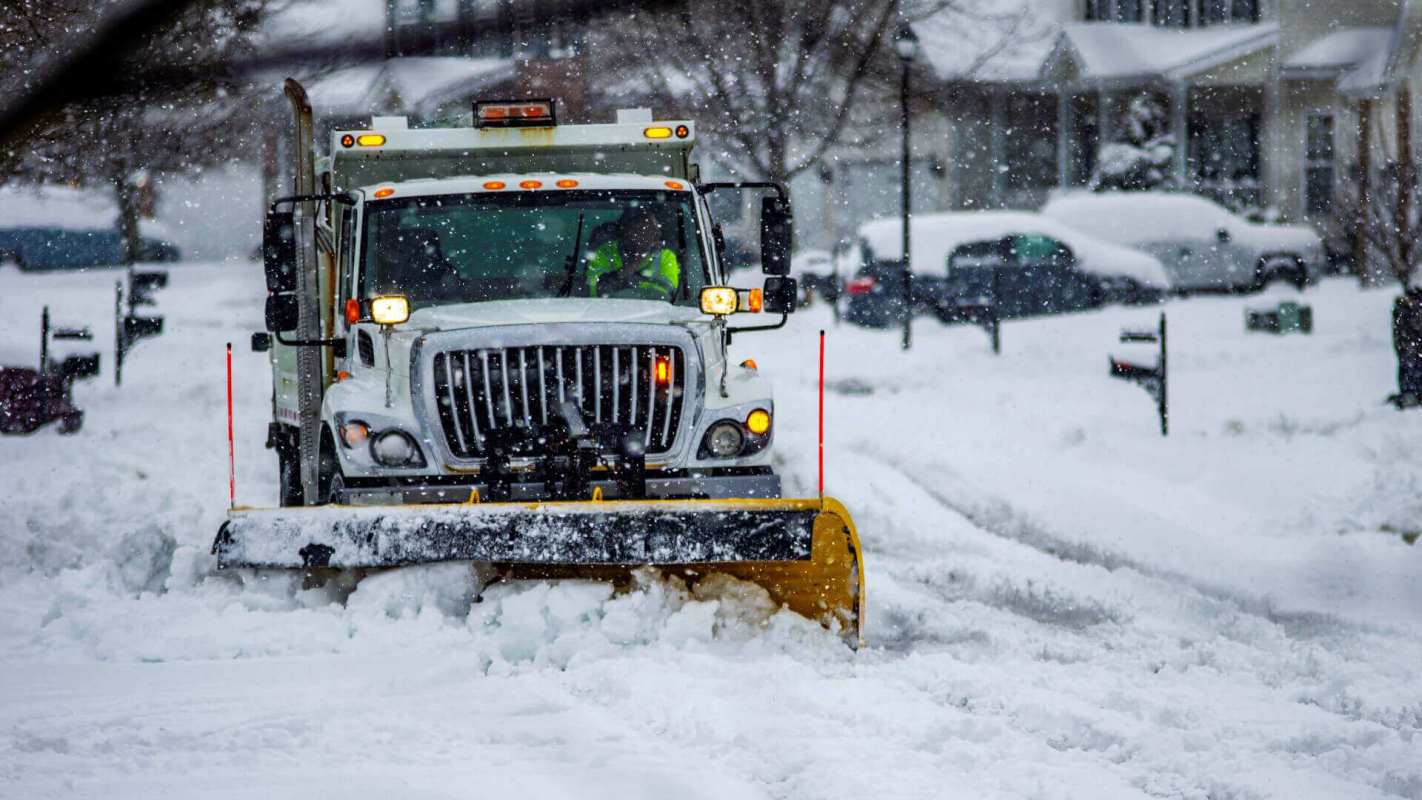
A major winter storm threatening a large swath of the U.S. from the Midwest through the Northeast may develop into a dangerous bomb cyclone, disrupting holiday travel plans for millions of Americans, meteorologists predict.
The storm could bring over a foot of snow in some areas, including the Great Lakes, causing dangerous driving conditions and widespread flight delays.
What is a bomb cyclone?
If you've read any headlines about the impending storm, you may be wondering what a bomb cyclone is.
A bomb cyclone happens through a process called "bombogenesis," which is a phenomenon that occurs when a storm's pressure drops 24 millibars (a unit measuring atmospheric pressure) or more in a span of 24 hours. This sudden decrease in pressure is a result of the storm rapidly intensifying.
According to AccuWeather, the term "bombogenesis" is a combination of the words "bomb" and "cyclogenesis."
"All storms are cyclones, and genesis means the creation or beginning. In this case, bomb refers to explosive development," the outlet explains. "Altogether the term means explosive storm strengthening."
Bomb cyclones are usually associated with intense winds, heavy snow and rain, severe thunderstorms, and large storm surges.
What causes a bomb cyclone?
Bomb cyclones are created when a cold air mass collides with a warm air mass, causing the warm air to rapidly rise and cool.
This creates an area of intense low pressure at the surface, which causes strong winds and heavy precipitation.
What makes a bomb cyclone so dangerous?
The rapid intensification of a storm can create hazardous conditions for those in its path, such as the potential for property damage, flooding, and life-threatening conditions.
According to CNN meteorologist Jennifer Gray, temperatures may drop so low in some places that "frostbite could begin in as little as five minutes on exposed skin."
Additionally, bomb cyclones can cause severe weather-related disruptions to transportation and communication networks, making it difficult for affected areas to respond to the effects of the storm.
How does climate change make winter storms more frequent?
Climate change is causing winter storms to become more frequent because warmer air holds more moisture, which results in heavier snowfall.
As temperatures rise, more moisture is evaporated from the ocean, rivers, and other bodies of water, and this moisture is carried in the air. And as this air moves inland and up into the atmosphere, it eventually reaches colder temperatures and forms clouds that can produce snowfall.
This additional moisture can cause heavier snow accumulations, resulting in more frequent winter storms.
Follow The Cool Down on Instagram and subscribe to our newsletter.