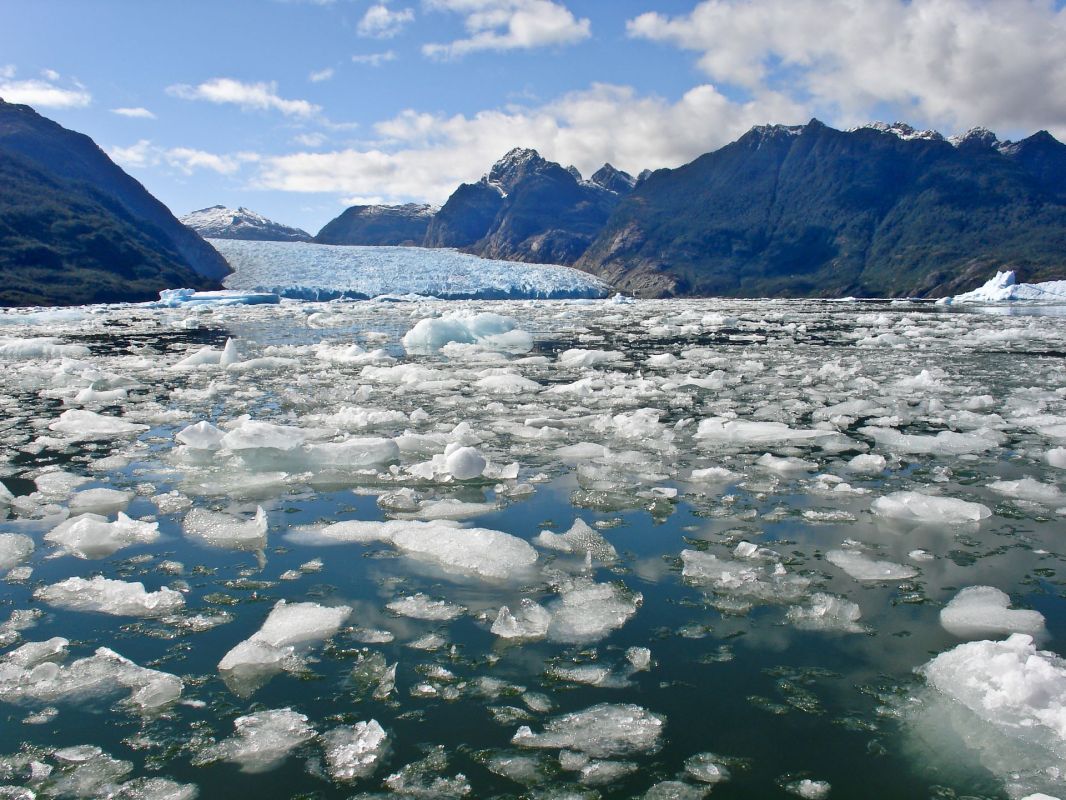
One of the largest glaciers in Greenland is melting much faster than experts had previously predicted, which could contribute to sea level rise at a dangerously quick pace, according to a study reported on by the Washington Post.
What's happening?
Scientists recently observed that the glacier, dubbed Petermann, is melting faster and possibly contributing to sea level rise twice as much as previously anticipated. Experts say that, in part, a rush of warm water flowing beneath the glacier during tidal cycles is causing the concerning uptick in melting.
"The melt rates reported are very large, much larger than anything we suspected in this region," Hélène Seroussi, a glaciologist, told the Post.
Petermann is one of the main channels through which other ice escapes from Greenland's interior and enters the ocean. If it were to disappear and release the ice behind it, that event could result in sea levels increasing by more than 1 foot, according to the Post's report.
The Petermann incident is part of a troubling trend. The average rate of sea level rise has been recorded at 0.06 inches per year between 1880 and 2013, but since 1993, it has been between 0.12 and 0.14 inches per year, or about twice as fast as the long-term trend, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Scientists say that Petermann is likely not the only glacier seeing this alarming melt rate.
Eric Rignot, one of the scientists involved in the recent study, told the Post that, "Probably a lot of other glaciers are in that situation, with tidal flushing."
Why are rising sea levels concerning?
Some of our most densely populated cities and towns sit on coastlines. As sea levels continue to rise, there could be devastating consequences to coastal habitats and communities. Rising sea levels could also contribute to more flooding and more intense storms.
Experts predict that, if the current rate of sea level increase remains, by the year 2100, hundreds of coastal communities could be effectively inundated by regular flooding.
Coastlines also provide a home to a significant number of wildlife — both animals and plants. As the oceans rise and coastlines shrink, living beings lose their habitats.
What can be done about rising sea levels?
The leading cause of rising sea levels is heat-trapping gases in the atmosphere. The ocean absorbs 90% of that heat, which results in warmer water and melting glaciers.
You can do your part to fight rising sea levels by adjusting your behaviors that contribute to heat-trapping gases.
This can mean leaving your car at home when possible and instead walking or biking to your destinations.
Consider shopping for clothes at thrift stores and consignment stores, instead of buying fast fashion.
Cutting back on red meat consumption is another great change, since beef production is one of the leading causes of the Earth overheating, according to Scientific American. Swapping just a few meat-based meals a week for plant-based ones can make a huge difference.
Ultimately, we need to rely less on dirty energy sources like coal, oil, and gas, which contribute greatly to the overheating of our planet, and use more clean, abundant energy sources like solar and wind power.
Join our free newsletter for cool news and cool tips that make it easy to help yourself while helping the planet.