The continued overheating of our planet is affecting life all over the world in some surprising ways and some disturbingly predictable ways. Falling into the latter category is the fact that the glaciers are melting.
What is happening?
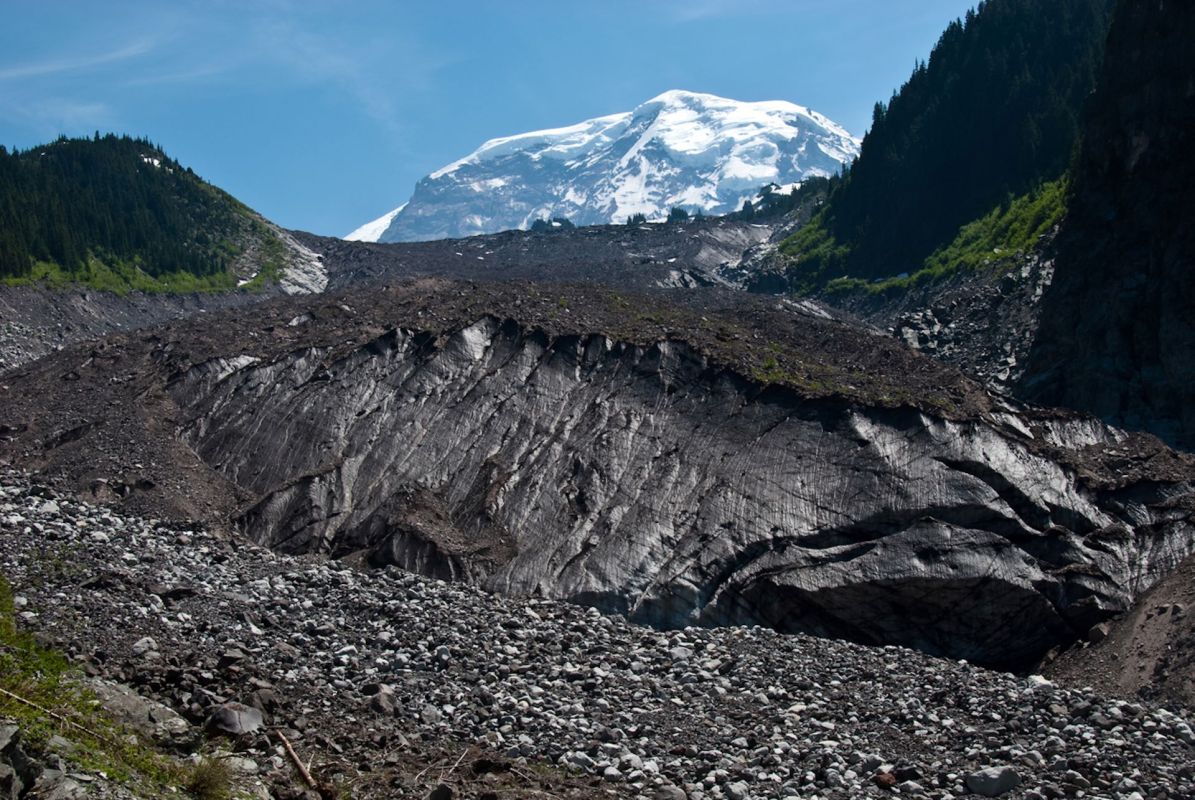
According to a new study from the National Park Service, the glaciers of Mount Rainier National Park in Washington state are in serious trouble, with one of the 29 already gone and two others "in serious peril."
All of the glaciers are steadily decreasing in size as temperatures rise overall and cold seasons grow shorter. "The glaciers at Mount Rainier are in a long-term demise," the study said.
Why is this concerning?
According to the Park Service study, "The long-term impacts of this loss will be widespread and impact many facets of the park ecosystem."
Some of the changes to the ecosystem have already been observed. Parts of mountains essentially held in place by the glaciers have tumbled down and wiped out old-growth forests. Rivers are changing course, and some types of plants are moving down the mountains, growing in places where they haven't before. And the changes are just beginning — the full effects of the glacier melt likely won't be known until they have already happened.
"Killing off a glacier is not something I take lightly," the park geologist who led the study told the New York Times. "Losing them is big."
What is being done about it?
The majority of the overheating of our planet is due to our reliance on burning dirty energy sources such as oil and gas. Until we are able to move past those outdated and harmful energy sources and replace them with things like wind and solar, the overheating will continue.
In addition, until the corporations that contribute the most heavily to air pollution are made to account for the ongoing damage they cause to the planet, it is unlikely that we will be able to prevent further irreparable impacts like the melting of the glaciers.
Join our free newsletter for cool news and cool tips that make it easy to help yourself while helping the planet.