A huge investment boost is set to allow a clean energy company to scale up its potential generation and storage capacity.
Fourth Power has welcomed $19 million in Series A funding that will go toward the construction of a 1 megawatt-hour-e prototype facility outside of Boston, as the company revealed in a statement published on Business Wire.
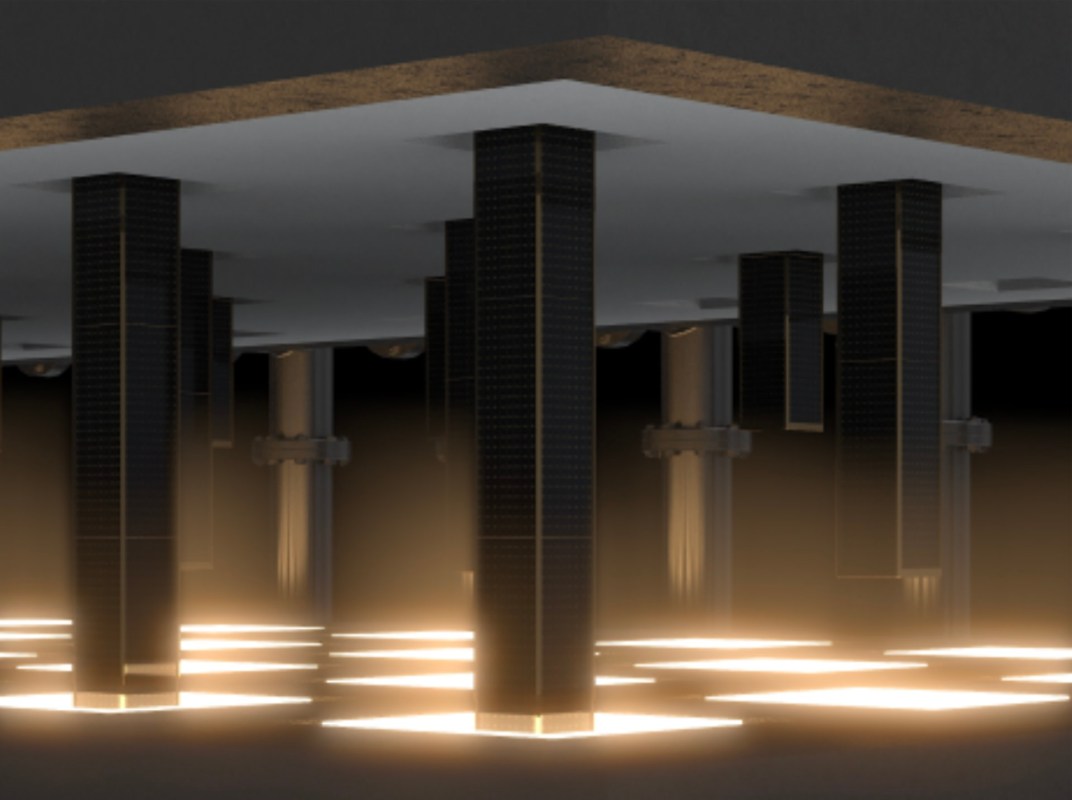
The company's thermal battery technology works by using renewable energy to heat carbon blocks to the point they "glow like the sun."
That heat can later be released as and when needed to provide electricity to the power grid, with thermophotovoltaic cells exposed to light to convert the energy.
The thermal battery has already broken a Guinness World Record, with the system developed by professor Asegun Henry recording the highest temperature pumping of liquid metal. The liquid tin reached a peak of 2,192 degrees Fahrenheit (1,200 degrees Celsius).
In addition to a larger facility, the funding will be used to conduct durability tests and hire new engineers to deal with the increasing demand for clean power.
The system helps to provide more control over the use of generated energy than other storage solutions, and the addition of more carbon blocks can increase storage duration.
"Our vision has always been to tackle climate change by making renewable energy — which is the most cost-effective form of power — a reliable resource for the grid to use at all hours of the day," Fourth Power CEO Arvin Ganesan said.
"Clean energy storage that is reliable and scalable will be a cornerstone of a zero-carbon future," Carmichael Roberts of Breakthrough Energy Ventures added.
It's yet another welcome development as the energy sector looks to move away from dirty fuel, which produces planet-warming pollution that encourages global heating.
And battery storage is particularly key, with renewable energy often dependent on certain weather conditions that aren't always consistent — with wind and solar as notable examples.
Lithium-ion is seen as one of the most effective materials for power storage, although there are problems with disposal after use and the potential of fires, while the material can also be expensive and difficult to source.
But sodium-ion is an alternative that can be produced at a fraction of the cost, and LG is producing single-crystal high-nickel cathodes that can increase both the capacity and life of batteries.
Meanwhile, solid-state batteries are inching closer to being used in electric vehicles, which will help to increase the range of travel on a single charge.
Improved battery technology will make a huge difference as various sectors swap polluting dirty fuel for renewable alternatives, and the new Fourth Power facility could be a real game-changer.
Join our free newsletter for weekly updates on the coolest innovations improving our lives and saving our planet.